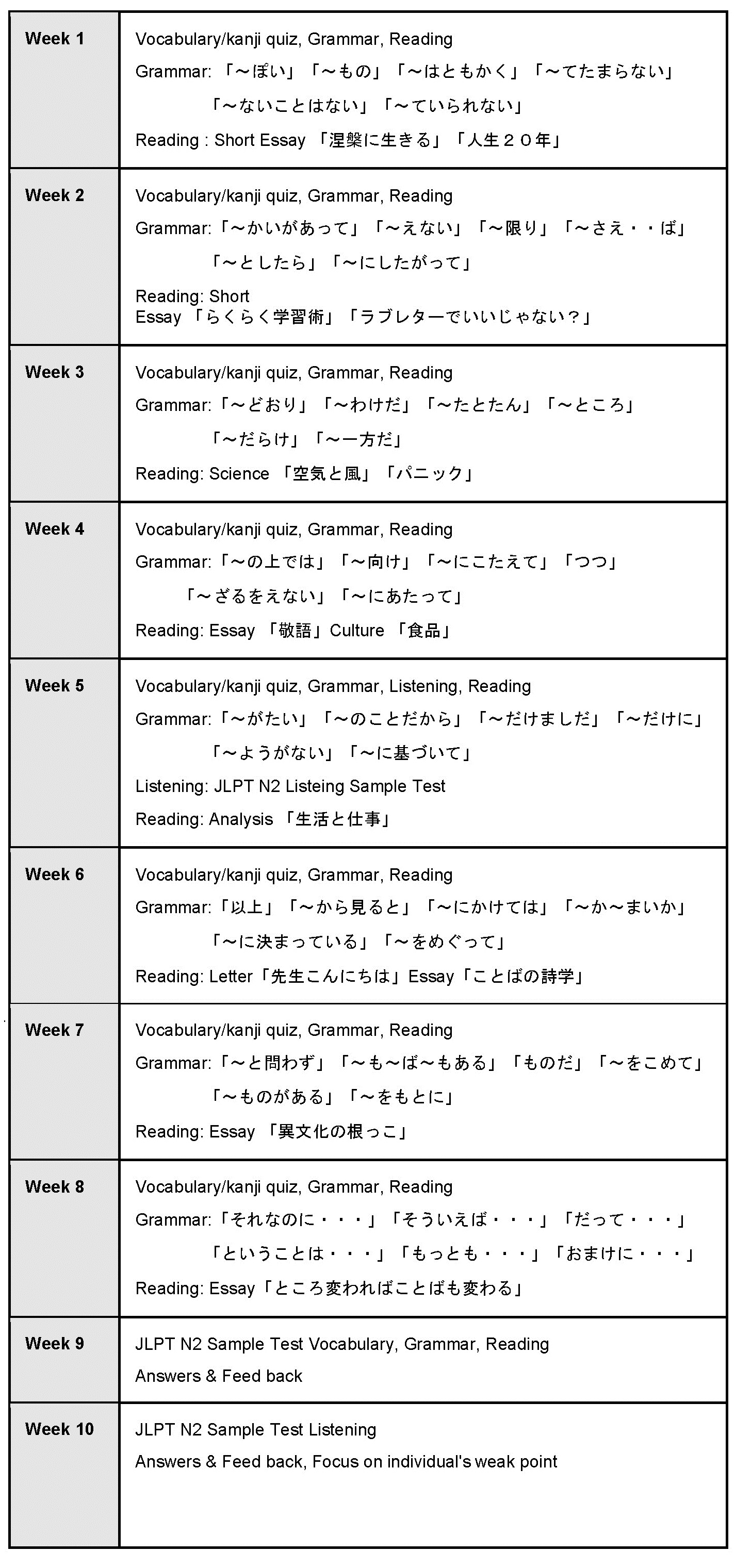
Learning the Japanese language can be a rewarding experience for anyone interested in understanding its rich culture and unique linguistic structure. Whether you're traveling to Japan, communicating with Japanese colleagues, or simply exploring a new language, mastering Japanese opens up countless opportunities. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the essential aspects of the Japanese language, helping you build a strong foundation.
Japanese is spoken by over 125 million people worldwide, primarily in Japan, but also by Japanese communities globally. As one of the most intricate languages, it offers a fascinating blend of grammar, writing systems, and cultural nuances. By understanding Japanese, you not only learn a language but also gain insight into Japanese traditions, values, and ways of thinking.
This article aims to provide everything you need to know about learning Japanese, from its basic structure to advanced concepts. Whether you're a beginner or someone looking to enhance their skills, we’ll cover all the important aspects step by step. Let’s dive in and explore the beauty of the Japanese language!
Read also:Stuart Scott And Kimberly Scott A Deep Dive Into Their Lives And Impact
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Japanese Language
- Writing Systems in Japanese
- Basic Grammar Rules
- Common Japanese Phrases
- Pronunciation Tips
- Learning Resources
- Cultural Context in Japanese
- Understand Japanese Through Media
- Challenges in Learning Japanese
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Introduction to Japanese Language
The Japanese language, known as Nihongo in Japanese, is an East Asian language spoken primarily in Japan. It is considered one of the most complex languages due to its unique writing systems, grammar rules, and cultural nuances. Understanding Japanese involves learning three different scripts: Hiragana, Katakana, and Kanji. Each script serves a specific purpose in the language, making it both challenging and fascinating to study.
Japanese has a rich history that dates back centuries, with influences from Chinese characters and Korean languages. Today, it is the official language of Japan and is also spoken by Japanese communities worldwide. With globalization, the demand for Japanese language learners has increased significantly, especially in business, tourism, and technology sectors.
Why Learn Japanese?
There are several reasons why understanding Japanese is beneficial:
- It enhances career opportunities in Japan and multinational companies.
- It allows you to communicate with native speakers and immerse yourself in Japanese culture.
- It improves cognitive abilities, as learning a new language stimulates the brain.
- It provides access to Japanese literature, media, and art forms.
Writing Systems in Japanese
One of the most distinctive features of the Japanese language is its writing system. Unlike English, which uses a single alphabet, Japanese employs three scripts: Hiragana, Katakana, and Kanji. Each script plays a crucial role in conveying meaning and context.
Hiragana
Hiragana is the basic phonetic script used for native Japanese words and grammatical elements. It consists of 46 characters, each representing a syllable. Hiragana is often the first script taught to beginners and is essential for reading and writing in Japanese.
Katakana
Katakana is another phonetic script used primarily for loanwords, foreign names, and onomatopoeia. Like Hiragana, it has 46 basic characters, but the shapes and usage differ. Katakana is often used to emphasize certain words or indicate their foreign origin.
Read also:Annie Cast 1982 A Comprehensive Guide To The Iconic Films Cast And Legacy
Kanji
Kanji refers to Chinese characters adopted into the Japanese writing system. There are thousands of Kanji characters, each with multiple meanings and readings. While mastering Kanji can be challenging, it is crucial for understanding written Japanese, as it provides context and depth to the language.
Basic Grammar Rules
Japanese grammar follows a Subject-Object-Verb (SOV) structure, which is different from the Subject-Verb-Object (SVO) structure used in English. This means that the verb typically comes at the end of the sentence. Understanding this basic structure is key to constructing correct sentences in Japanese.
Particle Usage
Particles are small words that indicate the grammatical function of other words in a sentence. Common particles include:
- wa: topic marker
- ga: subject marker
- o: object marker
- ni: direction or recipient marker
Verb Conjugation
Japanese verbs change form based on tense, politeness level, and other grammatical factors. For example, the verb "taberu" (to eat) can be conjugated as:
- tabemasu: polite form
- tabeta: past tense
- tabenai: negative form
Common Japanese Phrases
Learning common Japanese phrases is a great way to start practicing the language. Here are some essential phrases for everyday situations:
Greetings
- Konnichiwa: Hello (formal)
- Ogenki desu ka?: How are you?
- Sayonara: Goodbye
Polite Expressions
- Arigatou gozaimasu: Thank you very much
- Gomen nasai: I’m sorry
- Onegaishimasu: Please
Pronunciation Tips
Pronunciation is an important aspect of learning Japanese. The language has five vowel sounds and a relatively simple phonetic structure compared to English. However, mastering pitch accent and intonation can be challenging for beginners.
Vowel Sounds
Japanese vowels are pronounced consistently, unlike English vowels which can vary depending on context. The five basic vowel sounds are:
- A: as in "father"
- I: as in "machine"
- U: as in "rude"
- E: as in "bed"
- O: as in "open"
Pitch Accent
Pitch accent refers to the rising and falling intonation patterns in Japanese words. While not as critical as in tonal languages like Mandarin, pitch accent can affect meaning in Japanese. For example, the word "hashi" can mean "chopsticks" or "bridge" depending on the pitch accent.
Learning Resources
There are numerous resources available for learning Japanese, ranging from textbooks to online platforms. Choosing the right resources can make a significant difference in your learning journey.
Textbooks
Popular Japanese textbooks include:
- Genki: A comprehensive textbook for beginners
- Tobira: Focuses on intermediate learners
- Minna no Nihongo: Covers basic grammar and vocabulary
Online Platforms
Online platforms like Duolingo, Lingodeer, and NHK World offer interactive lessons and exercises for Japanese learners. Additionally, YouTube channels and podcasts provide valuable listening practice and cultural insights.
Cultural Context in Japanese
Understanding Japanese culture is essential for mastering the language. Japanese communication often relies on implicit understanding and context, which can be difficult for non-native speakers to grasp. Concepts like politeness levels, honorifics, and non-verbal cues play a significant role in Japanese interactions.
Politeness Levels
Japanese has multiple levels of politeness, ranging from casual to formal. The choice of vocabulary and grammar depends on the relationship between speakers and the social context. For example, using the polite form (-masu) is appropriate in most situations, while the casual form is used among close friends.
Honorifics
Honorifics are suffixes added to names or titles to show respect. Common honorifics include:
- -san: neutral and respectful
- -sama: highly respectful
- -kun: informal, often used for males
Understand Japanese Through Media
Consuming Japanese media is an effective way to improve language skills and cultural understanding. Movies, TV shows, anime, manga, and music provide authentic exposure to the language in real-life contexts.
Anime and Manga
Japanese anime and manga are popular worldwide and offer a fun way to learn the language. Shows like "Dragon Ball," "Naruto," and "One Piece" feature everyday conversations and cultural references that can enhance your understanding.
Music
Listening to Japanese music helps with pronunciation and vocabulary acquisition. Artists like Utada Hikaru, Arashi, and Aimer produce songs with catchy lyrics and meaningful themes.
Challenges in Learning Japanese
While learning Japanese can be rewarding, it also presents several challenges. The complexity of the writing system, grammar rules, and cultural nuances can be overwhelming for beginners. However, with dedication and the right resources, these challenges can be overcome.
Writing Systems
Mastering Hiragana, Katakana, and Kanji requires time and practice. Beginners often struggle with memorizing characters and their meanings. Using flashcards and apps like Anki can help with this process.
Grammar and Syntax
Japanese grammar differs significantly from English, which can be confusing for learners. Understanding sentence structure, particle usage, and verb conjugation takes practice and patience. Regular exposure to the language through reading and listening can improve comprehension.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Understanding the Japanese language opens doors to a rich cultural world and countless opportunities. From its unique writing systems to intricate grammar rules, mastering Japanese requires dedication and persistence. By following the tips and resources outlined in this guide, you can build a strong foundation and progress in your language journey.
We encourage you to take the next step by exploring the resources mentioned and practicing regularly. Leave a comment below to share your experiences or ask questions. Don’t forget to check out other articles on our site for more language learning tips and insights. Happy learning, and best of luck on your Japanese journey!